Indexing is a technique in databases that can help speed up searches. When managing a database, depending on the workload that will run on the database, you might decide to create indexes for certain tables.
In this example, let’s imagine you manage a library, and thus we have tables to manage books, customers, and employees. Each of these tables may have indexes depending on their workloads.
Later you might want to see what indexes exist in that table. There are 2 different methods to list down all the indexes present in the Postgres database - using \di command and using pg_indexes SQL query. In this tutorial, we will examine these two techniques and understand their differences.
The \di command
Step 1 - Open your terminal and connect it to your desired Postgres database. Follow our guide to set up the connection with the database.
Step 2 - To list down all the indexes, use the \di command.
\di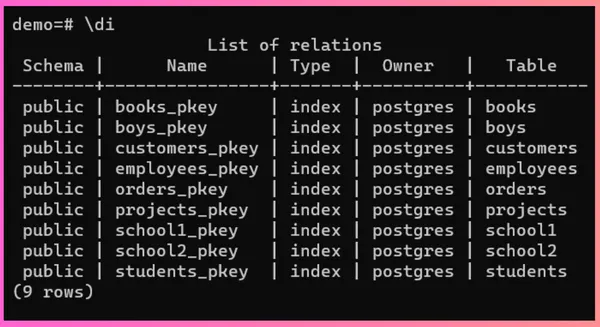
This command returns the table of all indexes present in the database consisting of details like Schema, Name, Type, Owner, and Table.
The \di command (docs) can accept a pattern parameter, where only indexes matching that pattern will be listed.
Using pg_indexes SQL query
Postgres comes with a system view pg_indexes that can be used to list down all the indexes. You can use this SQL query to display the list of all indexes.
Step 1 - Open your terminal and connect it to your desired Postgres database. Follow our guide to setup the connection with the database.
Step 2 - To list down all the indexes, use this sql query:
SELECT indexname AS index_name,
tablename AS table_name
FROM pg_indexes
WHERE schemaname = 'public';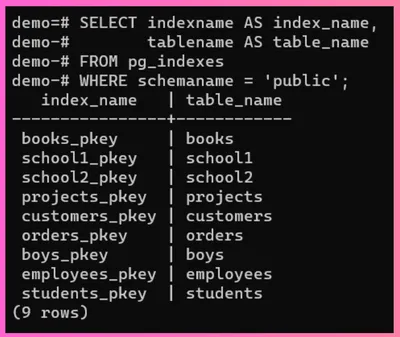
You can run this same command in the pgAdmin tool and it will return the same results.
Here we have defined index_name and table_name as alias names, but it’s totally optional. If you want, you can avoid using them.
index_name shows the name of the index stored and table_name shows the name of the table stored at that particular index.
Here, we have displayed the indexname and tablename from the pg_indexes. However, it also retains some additional data too. To know more about it, check their official documentation.
Conclusion
In this guide, we discussed different methods to list down all the indexes present in Postgres.
Want to expand your knowledge of Postgres? Explore our additional guides.
Curious about extensions? Check out our blog posts to delve into Tembo’s extensions.
