Imagine you are managing a large record of thousands of users having multiple details about users stored in a CSV (Comma Separated Value) file. Your objective is to load this entire repository of user data from the CSV file into a PostgreSQL table.
Manually inserting details of each of these users in the Postgres table would be extremely tedious and error-prone. Fortunately, Postgres comes with the flexibility to directly import a CSV file to a table with a single command and within a few seconds.
There are mainly two ways to import the CSV file - Via a SQL query and via the PgAdmin tool.
Using SQL query
Step 1 - Prepare your CSV file. Create the table in Excel and save your desired data of users in it.
Save your CSV file on the machine where your database is running. Postgres needs to access the CSV file on the filesystem to be able to load it.
Step 2 - Open your terminal and connect it to your desired Postgres database. Check out our guide on how to connect to Postgres.
Step 3 - Create a table in the Postgres database into which you want to copy the data. To create the table, run the following command in your terminal:
CREATE TABLE table_name (column1 data_type, column2 data_type, column3 data_type, …);A critical point to note is, the columns you will specify in this table should have the exact same name and data type and in the exact same order as created in the table in the CSV file.
Step 4 - To import the CSV file, Postgres has a COPY command. The COPY command allows us to move/copy the data of a standard file into Postgres.
Execute the following COPY command to copy the CSV file data to the Postgres table:
COPY table_name FROM 'path' WITH (FORMAT CSV, HEADER)In this command-
- Replace the
table_namewith the name of table you have previously created in the Postgres database - Replace the
pathwith the path of CSV file FORMAT CSVrepresents the file type of CSV fileHEADERrepresents the first row of the CSV file holding the names of the column. If there is not any headers in the CSV file, you can ignore addingHEADERto the command
In this example, we have passed just table_name, path, FORMAT CSV, and HEADER arguments in the COPY command; however it can accept many other arguments to specify the file and data that you want to load into Postgres.
Check out the official documentation to learn more about the COPY command.
Using PgAdmin tool
Step 1 - Open the PgAdmin tool on your device and in it, open the Query tool in your desired database.
To do that, expand the Servers (on left sidebar) and direct to → PostgreSQL → Databases → Your_desired_database → Schemas.
Right Click on Schemas and select the Query tool option.
Step 2 - Just like the previous method, you must create a table with the same columns and names as the data in the CSV file. To create the table, run the following command in query tool:
CREATE TABLE table_name (column1 data_type, column2 data_type, column3 data_type, …);Step 3 - Right click on the created table (present under the tables section), and select the Import/Export Data option. The Import/Export Data Prompt box will appear on the screen.
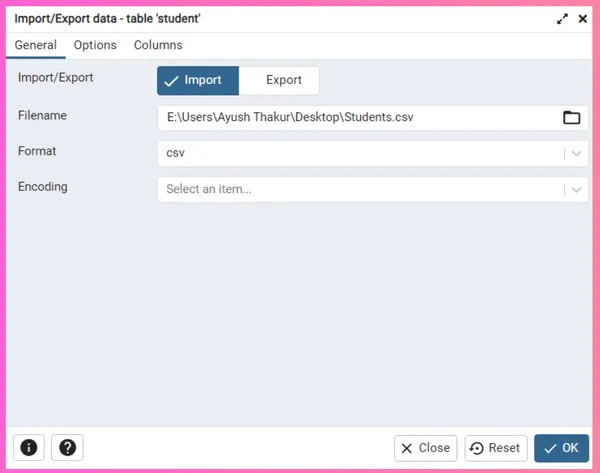
Step 4 - Select your desired CSV file in the Filename option and select csv in Format option. Now, go to the Options section and toggle the Header option to On, if your CSV file table has headers in it.
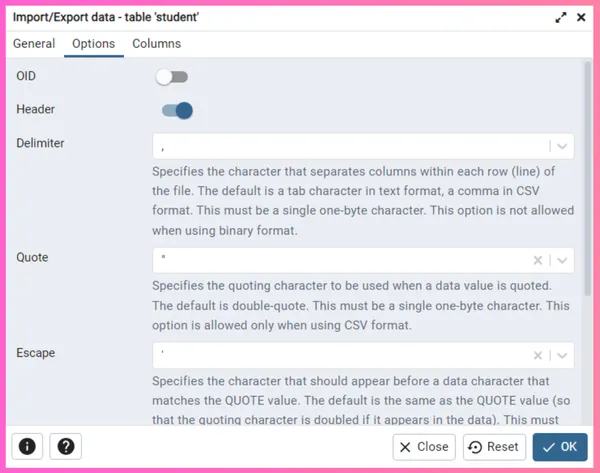
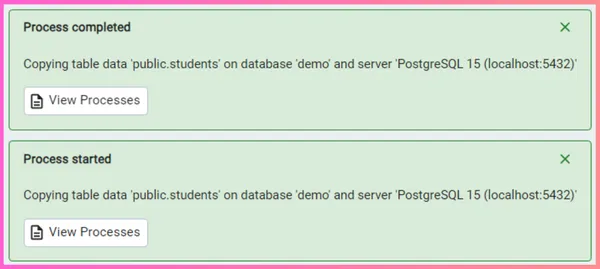
Step 5 - Click the OK button to initiate the import process. Upon successful completion of the data import, a prompt box will confirm the successful import of your data.
Conclusion
In this guide, we understood the two different methods to import a CSV file into a Postgres table.
Interested to learn more about Postgres utilities? Check out our collection of guides to continue learning about Postgres.
