Postgres provides the flexibility to add multiple users to a specific database, allowing for fine-grained control over user access and permissions. This also helps in maintaining the security of the database and can help prevent serious issues if a user account is compromised.
Suppose you are working on a company’s project and you want to add your team members to the project so that they can work on it; however you may not want to grant full access to the database to each user (e.g. prevent PII access, grant read-only access, etc). In such a case, you can create specific users for each of your team members and define specific access rules and privileges for them. Let’s see how you can do this.
Using psql
Step 1 - Open your terminal and connect it to your desired Postgres database. Follow our guide to see the whole process.
Step 2 - Execute the following SQL query to create a new user in the database:
CREATE USER username WITH PASSWORD 'password';
Make sure to replace the username and password with the username and password that you want to keep in the database.
Postgres comes with a SUPERUSER keyword to give a new user all the superuser privileges:
CREATE USER username WITH PASSWORD 'password' SUPERUSER;
A superuser has full control over the entire database. Superuser has the special privileges on the whole database and is allowed to perform administrative operations that other normal users are restricted to perform. However, keep in mind that you should only grant the privileges that your users strictly need.
Step 3 - Exit the database after the new user has been created. To do that, you can use the \q command.
\q
Using the createuser command
Postgres comes with a command line utility called createuser. It’s a simple, but powerful program that helps you create new Postgres users quickly, and allows you full control of user access management and privileges. Here’s how you can create a user with this command:
Step 1 - Open your terminal. If you are on a Unix-based system, then you first need to log into the operating system as a user with the right privileges to connect to the database (usually “postgres”). To do this execute the following command:
sudo -i -u postgres
If you are on Windows, you can skip this step.
Step 2 - Use the createuser command to create a new user in the Postgres database:
createuser --interactive --pwprompt username
Make sure to replace the username with the username that you want to keep.
Once you execute this command, it will ask you to set a password and define the role for the new user.
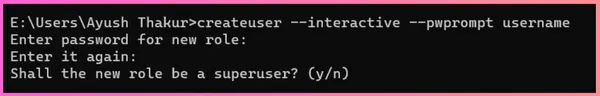
In this instance, we’ve provided only the username in the createuser command, however it’s worth noting that the createuser command allows users to include additional arguments like -a role, -c number, –echo, and others to specifically define the role of the new user.
Check their official documentation to learn more about the createuser command.
Conclusion
In this guide, we studied the step-by-step process to create a new Postgres user.
We recommend you check out our other Postgres guides and visit our blog section to stay updated on our upcoming projects and new additions.
